Understanding Ink Migration

Understanding Ink Migration
What ink migration?
Ink migration is the unintended process of ink bleeding through packaging and transferring from the packaging, onto or into the customer's goods such as food, medicines, or health and beauty products.
This comes with a multitude of risks when this happens. It could put the customer's health at risk, it will change the flavour and odour of the products and could possibly be toxic. It violates regulations and that can lead to a damaged reputation for your company.
The types of ink migration
There are 3 types of Ink migration: Set-off Migration, Diffusion Migration and Gas-phase Migration.
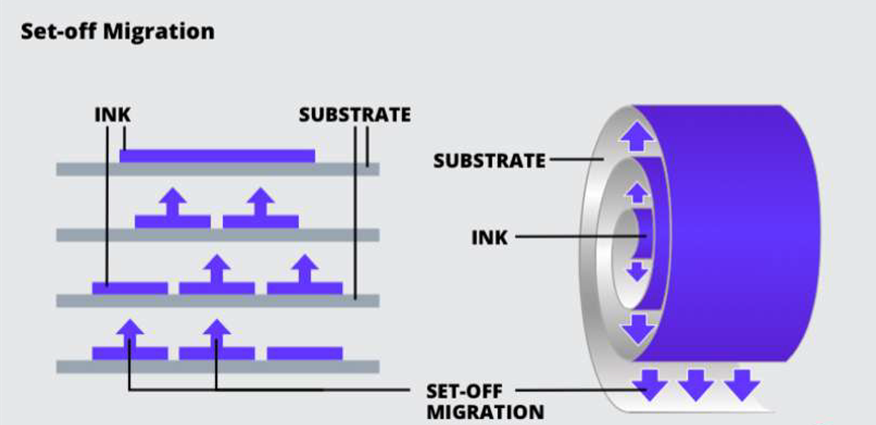
SET-OFF Migration:
Chemicals from the printed side of one package or label transfer to the reverse side, where it can contact the food
Set-Off Migration can be caused by re-rolling or stacking printed packaging materials and it can also occur if the ink has not completely cured or dried. This can be prevented by ensuring the curing has been completed before stacking or re-rolling, keeping the total ink coverage below 300% and making sure that the inks being used have been tested.
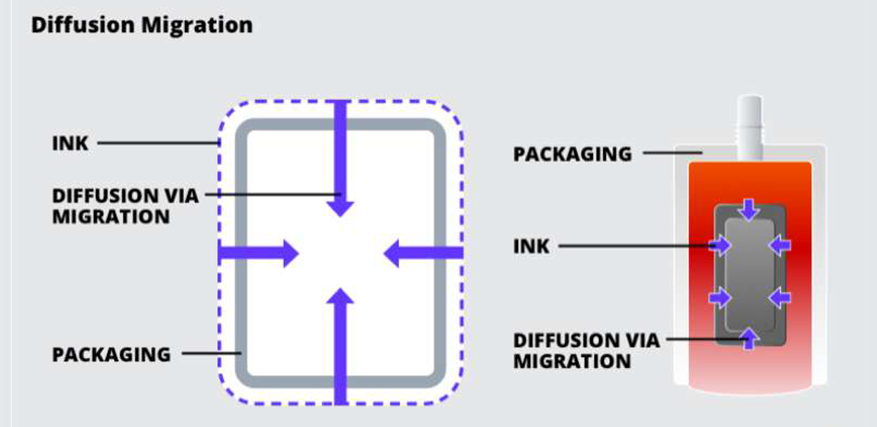
Diffusion Migration:
Diffusion is where the ink passed through the packaging substrate and directly contacts the food, pharmaceuticals, or beautify product.
Causes of Diffusion Migration are Improper curing or drying, and inferior substrate. This can be solved by using an absolute barrier such as glass or metal and using inks that have been tested for conditions when using plastic packaging.
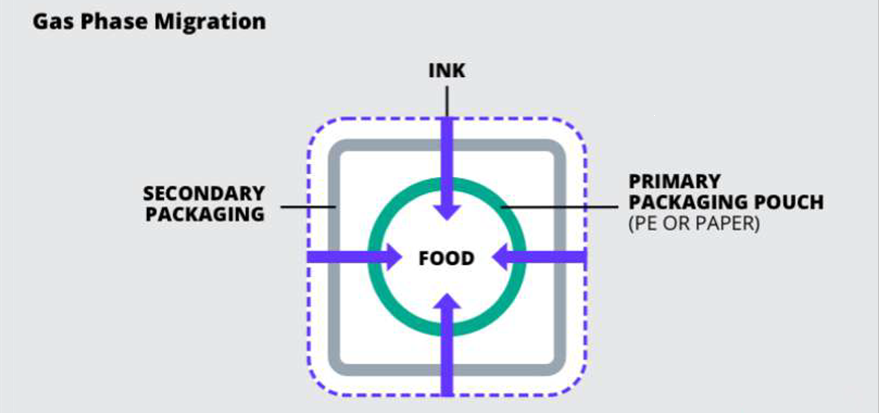
Gas Phase:
Volatile substances transfer in the space between the packing and the product
Knows causes of this are the printing environment, incomplete curing, post-packaging environment effects and using inks with VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds). Ways around this include matching inks to the primary packaging material, which is usually based on their party testing. And using mineral-oil-free ink for secondary packaging.
Quality Control
When talking about quality control in the ink industry and printing inks on the packaging. It’s often referred to as the 10 GMPs (Good Manufacturing Practices). These are:
1: Procedures
- Detailed written procedures (easily understood)
- Track performance
- Verify calculations
- Tracing and tracking systems
2: Plant & Facilities
- Free from contamination risk
- Operated in a suitable location
- Built to industry standards
- Designed to minimize risk
- Easy to clean and maintain
3: Documentation & Record Keeping
- Integrity of standard operating procedures
- Design history file (DHF)
- Employee training
- Manage document changes
- Designed to minimize risk
- Easy to clean and maintain
4: Personnel
- Trained upon hiring
- Qualified for specific jobs
- Understanding of GMPs
- Ongoing annual training
- Traffic patterns for guests and employees
5: Sanitation Programs
- Outline policies and processes
- Avoiding cross contamination
- Create master schedule
6: Water Potability
- Monitor sources
- Ensure proper plumbing
- Monitor ice
- Minimum annual testing
7: Allergen Control
- Stages of prevention
- Complete ingredient lists
- Dedicated storage/warehousing
- Dedicated equipment and utensils
- Cleaning procedures
8: Equipment Utensils & Maintenance
- Well-designed preventive maintenance program
- Sanitation procedures
- Investigating, documenting equipment failures
- Procedures for bringing new equipment online
9: Receiving, Warehousing, Shipping
- Tracking from arrival to departure
- Storage in proper and sanitary conditions
- Map of designated storage areas
- Supplier protocols
- Acceptance and rejections criteria
10: Recall & Tracking Systems
- System for tracking through the supply chain
- Lot coding raw materials
- Established testing system
- Fast and efficient recall processes
- Practice mock recalls
Inks For Food Packaging
- Water-Based
- Low-Migration UV/LED Curable
- Electron-Beam Curable
- Bio-Ink Mineral Oil Free
Water-Based
- Environmentally friendly with no or low odours
- Standard formulations available for paper and other porous materials
- Nano pigment inks for flexible packaging and thin film
Low-Migration UV/LED Curable
- High purity of ink components
- Specially formulated photo initiators
- High-quality results
- LED curing produces less heat
Electron-Beam Curable
- No photo initiators used
- Low energy consumption
- No heat generated
- High visual appeal
- Instant curing
Bio-Ink Mineral-Oil-Free
- No hazardous pollutants (HAP)
- Near-zero VOCs
- Rich, deep colours for single-pass applications
- Easily scannable barcodes
- Compostable
